You can let users sign in to your app with their Google accounts on devices withlimited input capabilities, such as Internet-connected TVs.
The device driver should check for any contentions before accessing the port. However, using a driver such as PortTalk can become quite inefficient. Each time an IOCTL call is made to read or write a byte or word to a port, the processor must switch from ring 3 to ring 0 perform the operation, then switch back. Google USB Drivers are required to connect Google Pixel or Nexus devices to Windows PC using a USB cable. You will need these drivers to transfer files or sync data on your Pixel/Nexus device, and especially when working with the Android ADB and Fastboot tools. The device must be capable of displaying a 40-character URL and a 15-character user code, along with instructions to the user. The device must be connected to the Internet. Get a client ID and client secret. Your app needs an OAuth 2.0 client ID and client secret to make requests to Google's sign-in endpoints.

The app displays a short code and sign-in URL to the user. Then, the user opensthe sign-in URL in a web browser, enters the code, and grants the app permissionto access the user's sign-in information. Finally, the app receives confirmationand the user is signed in.
To use this sign-in flow, the app must run on a device that meets the followingcriteria:
- The device must be capable of displaying a 40-character URL and a 15-characteruser code, along with instructions to the user.
- The device must be connected to the Internet.
Get a client ID and client secret
Your app needs an OAuth 2.0 client ID and client secret to make requests toGoogle's sign-in endpoints.
To find your project's client ID and client secret, do the following:
- Select an existing OAuth 2.0 credential or open the Credentials page.
- If you haven't done so already, create your project's OAuth 2.0 credentials by clicking Create credentials > OAuth client ID, and providing the information needed to create the credentials.
- Look for the Client ID in the OAuth 2.0 client IDs section. For details, click the client ID.
If you are creating a new client ID, select theTVs and Limited Input devices application type.
Obtain a user code and verification URL
Once a user requests to sign in using a Google Account, you obtain a user codeand verification URL by sending an HTTP POST request to the OAuth 2.0 deviceendpoint, https://oauth2.googleapis.com/device/code. Include yourclient ID and a list of the scopes you need with the request. If you only wantto sign in users with their Google accounts, request only the profile andemail scopes; or, if you want to request permission to call asupported APIon behalf of users, request the required scopes in addition to the profileand email scopes.
The following is an example request for a user code:
Using curl:
The response is returned as a JSON object:
Your app displays the user_code and verification_url values to the user,and, at the same time, polls the sign-in endpoint at the specified intervaluntil either the user signs in or the time specified by expires_in has passed.
Display the user code and verification URL
After you receive a user code and verification URL from the device endpoint,display them and instruct the user to open the URL and enter the user code.

The values of verification_url and user_code are subject to change. Designyour UI in a way that can handle the following limits:
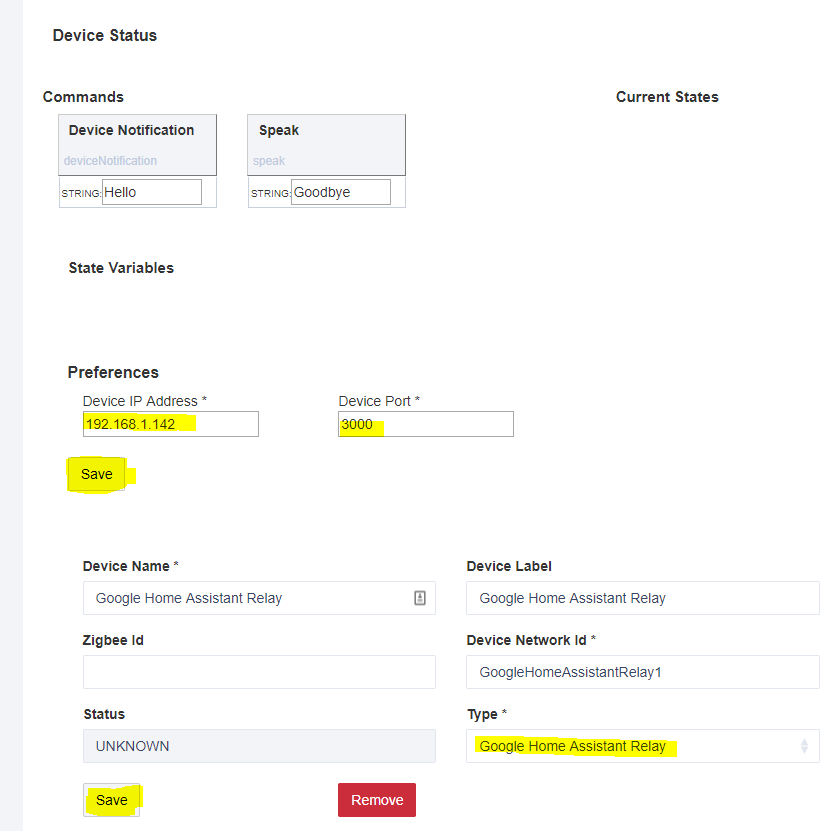
Com Port Driver
user_codemust be displayed in a field wide enough to handle 15W-sizedcharacters.verification_urlmust be displayed in a field wide enough to handle a URLstring that is 40 characters long.
Both strings can contain any printable character from the US-ASCII characterset.
When you display the user_code string, don't modify the string in any way(such as changing the case or inserting other formatting characters), becauseyour app might break if the format of the code changes in the future.
You can modify the verification_url string by stripping off the scheme fromthe URL for display purposes if you choose. If you do, be sure your app canhandle both 'http' and 'https' variants. Don't otherwise modify theverification_url string.
When the user navigates to the verification URL, they see a page similar to thefollowing:
Free Device Driver Downloads
After the user enters the user code, the Google sign-in site presents a consentscreen similar to the following:
If the user clicks Allow, then your app can obtain an ID tokento identify the user, an access token to call Google APIs, and a refresh tokento acquire new tokens.
Obtain an ID token and refresh token
After your app displays the user code and verification URL, begin polling thetoken endpoint (https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token) with the devicecode that you received from the device endpoint. Poll the token endpoint at theinterval, in seconds, specified by the interval value.
The following is an example request:
Using curl:
If the user has not yet approved the request, the response is as follows:
Your app should repeat these requests at a rate that does not exceed the valueof interval. If your app polls too quickly, the response is as follows:
Once the user signs in and grants your app access to the scopes you requested,the response to your app's next request includes an ID token, an access token,and a refresh token:
Upon receipt of this response, your app can decode the ID token to get basicprofile information about the signed-in user, or send the ID token to your app'sbackend server to securely authenticatewith the server. Also, your app can use the access token tocall the Google APIsthat the user authorized.
ID and access tokens have limited lifetimes. To keep the user signed in beyondthe tokens' lifetimes, store the refresh token and use it torequest new tokens.
Get user profile information from the ID token
You can get profile information about the signed-in user by decoding the IDtoken with any JWT-decoding library. Forexample, using the Auth0 jwt-decodeJavaScript library:
Note: Because you received the ID token directly from Google, you can decode thetoken without validating it. Whenever you receive an ID token from a sourceother than Google, such as from a client app to your backend server, you mustvalidate the token to ensure its authenticity. SeeAuthenticate with a backend server.More information
Google Port Devices Driver
- To keep users signed-in beyond the lifetime of an ID token, seeRefreshing an access token.
- If you need to authenticate with a backend server, seeAuthenticate with a backend serverfor information on doing so securely.